And More… Check my CV for Additional Work and Contact me for Potential Collaborations
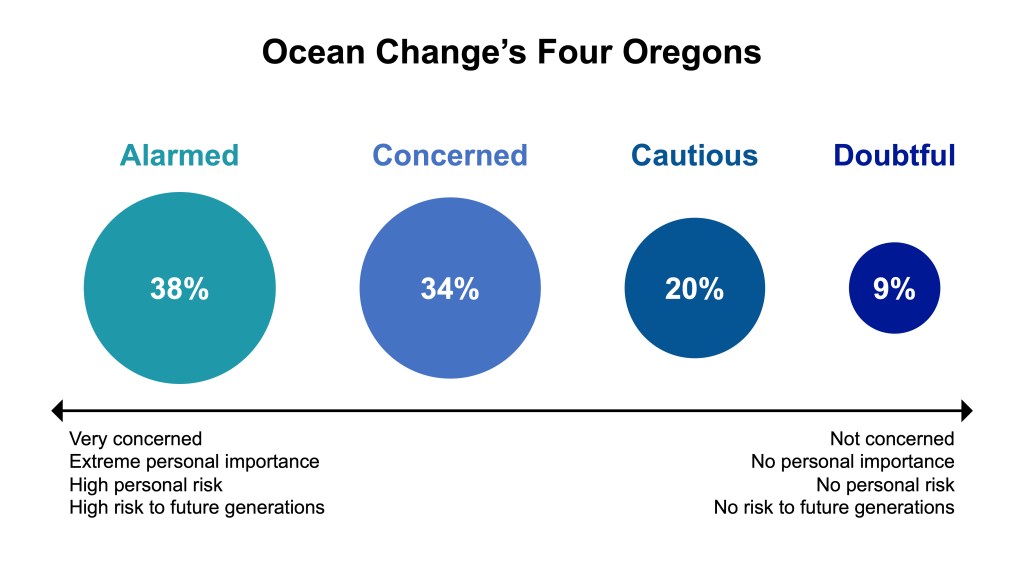
Oregon’s Four Audience of Ocean Change Beliefs
ABSTRACT
Climate change’s impacts on the oceans (“ocean change”) threaten people globally. Climate action is needed at multiple scales, from individual to collective action, and yet there is limited research on what motivates this action in response to ocean change. In this study, we conducted an online survey of residents of the state of Oregon, United States (n = 1414), to assess concerns, personal importance, and risk perceptions regarding ocean change and explore potential psychological cognitions to target in action-oriented communication efforts. Our latent class analysis identified four distinct audience subgroups ranging from individuals who are Doubtful (9 %) about ocean change to those who are Cautious (20 %), Concerned (33 %), and Alarmed (38 %). Audience subgroups varied in their climate action intentions and associated psychological cognitions (i.e., psychological distance, efficacy beliefs, social norm perceptions). The climate action intentions of the Alarmed and Concerned were positively predicted by all cognitions, those of the Cautious were significantly predicted by social norms (β = .15, p = .002) and efficacy beliefs (β = .34, p < .001), and those of the Doubtful were only predicted by efficacy beliefs (β = .23, p < .001). Across all four audiences, efficacy beliefs were strongly associated with intended climate action (β = .30, p < .001), suggesting efficacy beliefs may be a practical cognition to target in broad audience communication efforts on ocean change. These findings reinforce the importance of targeting specific psychological cognitions and, ideally, distinct audiences in ocean change communication efforts intending to motivate widespread climate action.
Psychologically Wise Communication for Climate Action
ABSTRACT
Widespread climate action is broadly recognized as necessary to reduce climate change impacts on oceans (“ocean change”), but threats to ocean ecosystems are commonly perceived as distant, irrelevant, and unchangeable. Communicating about ocean change, therefore, requires message framing strategies targeting evidence-based psychological precursors to behavior. In a pre-registered case study of coastal visitors in Oregon, United States (n = 2414), we tested the influence of psychologically wise message about ocean change on climate action intentions. We primarily focused on influencing relational organizing: people’s willingness to encourage others to act. A behavior-specific message targeting relational organizing efficacy beliefs significantly but weakly increased intentions for relational organizing regarding ocean change compared to a control. Neither a connectedness to coast (place-based) message nor an ocean acidification (proximate threat-based) message had detectable effects on intentions. Our results suggest that targeting relational organizing efficacy may increase climate action intentions for the protection of coastal ecosystems.
This project is a collaboration between the Human Dimensions Lab at Oregon State University and the Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife‘s Oregon Marine Reserves.


Bycatch Avoidance in Tropical Tuna Purse Seine Fisheries
ABSTRACT
The incidental capture of non-target species (bycatch) in tuna fisheries impacts some marine vertebrates, particularly species with vulnerable life histories such as manta and devil rays (mobulids). There is broad interest in reducing mobulid bycatch in tuna purse seine fisheries, with existing efforts mainly focusing on reducing post-capture mortality rates. We explore a novel potential pre-capture mobulid bycatch avoidance strategy for the tuna purse seine fishery using communication between fishing vessels and associated spotter helicopters. We conducted a survey of tuna purse seine helicopter pilots, spotters, and fishers operating in the eastern Pacific Ocean (n = 33) to ascertain the ability of helicopter crew to detect mobulids prior to capture and communicate bycatch avoidance with vessel crew. Results indicate over half of the helicopter crew report being “always” or “sometimes” able to sight and identify mobulids and that helicopter crew regularly communicate mobulid sightings to the vessel already. Given that an average of 63% of class-6 vessel trips between 2017 to 2022 carried onboard helicopters, our results suggest that helicopter-vessel communication could be feasible and scalable for mobulid bycatch detection, enabling potential bycatch avoidance and early alerts for proper handling protocols. We also identify the potential use of helicopter detection to improve research efforts for mobulid conservation (e.g., data collection of population and habitat observations). This study is the first to investigate the utility of helicopter-vessel communication as a bycatch mitigation strategy for elasmobranchs and identifies research and management directions that could be further investigated to avoid bycatch of mobulids.


This project was a collaboration between researchers at the University of California – Santa Cruz, the International Seafood Sustainability Foundation, the Inter-American Tropical Tuna Commission, Mobula Conservation, and Manta Trust.





An Interactive Map of Ocean Change Opinions in Oregon
As a Science to Action Fellow for the U.S. Geological Survey National Climate Adaptation Science Center, I developed an online interactive database that maps Oregonians’ opinions, beliefs, and perceptions about ocean change for local natural resource managers, policy-makers, and communicators to use as a decision support tool.


Who is Engaged with Oregon’s Marine Reserves?
This report presents the findings of a collaborative project between the Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife (ODFW), Oregon State University (OSU), and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) to evaluate public perceptions in Oregon of ocean acidification, engagement in climate action, and how these may be related to perceptions of the marine reserves.
















